The Institute
The Institute has several research laboratories that facilitate the development of different types of solutions, such as the construction of operational software prototypes, platforms for the deployment of communications, solutions for the analysis of communications protocols in a wide range of frequencies, and advanced environments in which to develop forensic computing, among others.
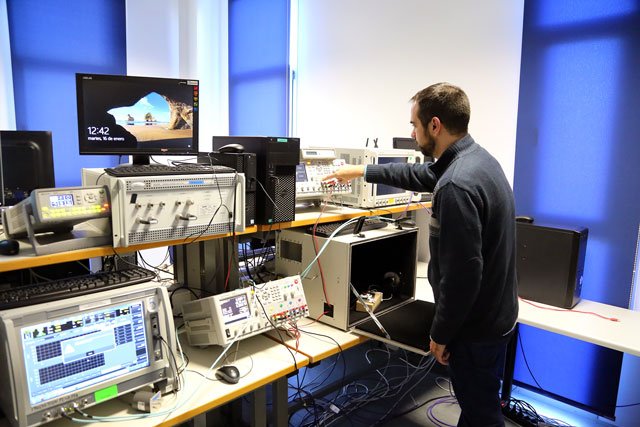
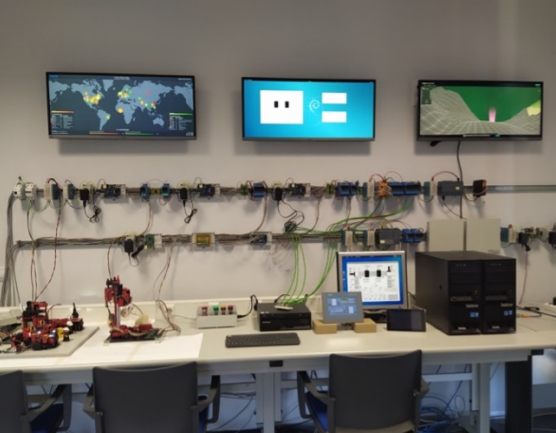
Testing laboratory for mobile communications
The MORSE team is operating an infrastructure for research in 4G/5G technologies in two environments, combining commercial carrier grade and open source network components. The indoor setup is based on a Keysight emulators for 4G and 5G plus anchoic chambers, commercial user devices and advanced monitoring equipment (energy, spectrum, etc.). Currently, emulators support frequency bands from 800MHz to 26GHz. The outdoor deployment is based on a collaboration with Telefonica, with NOKIA cells on the UMA campus. These cells are connected to local core networks in order to provide a full private network. They support LTE and 5G NR to implement the Non Stand Alone and Stand Alone modes. The distributed configuration with base unit plus remote heads allows it to move towards a C-RAN deployment. The support of several network identifiers (PLMNs) with MOCN technologies is used to implement a first level of slicing at the radio, offering up to six operators at the same time. Telefonica offers the commercial LTE spectrum for LTE (2600 MHz FDD) and 5G (3500 MHz TDD) for exclusive use on the campus. On top of that, ITIS has obtained authorization to use 26GHz band for milimiter wave. The virtualized infrastructure with support for traditional virtual machines and containers supports any approach to service deployment. This setup is expanded to the city centre by means of an agreement with the city of Malaga, so ITIS can expand their trials to this relevant area for experimentation, testing and validation in a more crowded environment.
Cybersecurity Infrastructure
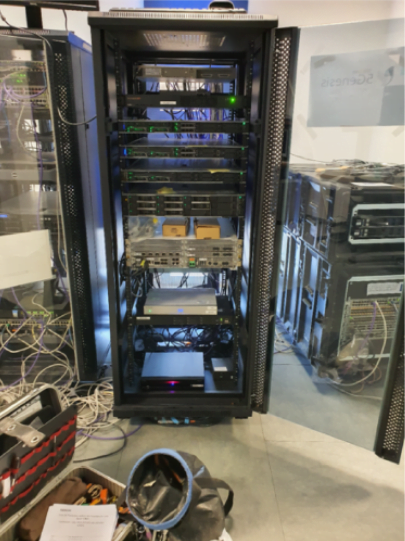
IITIS has a specific cybersecurity laboratory led by the NICS Lab group. This laboratory deploys a cybersecurity infrastructure containing a test-bed to support industrial environments, as well as capabilities and support for the deployment of solutions in blockchain networks and environments for forensic analysis.
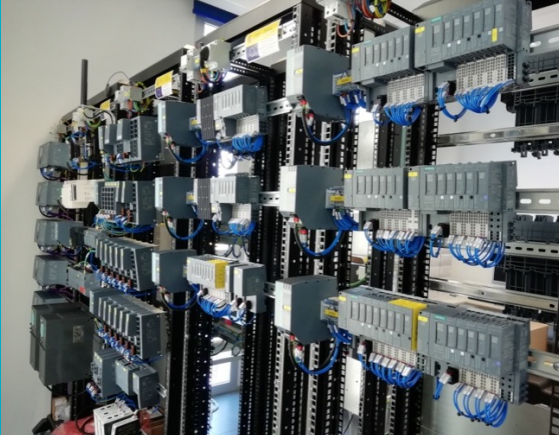
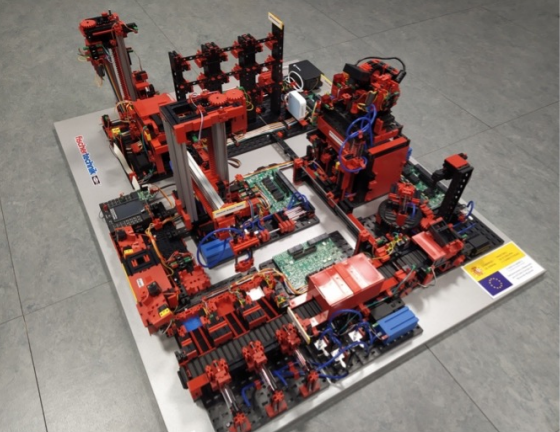
The industrial testbed is designed to host new Industry 4.0 technologies. The infrastructure consists of three industrial cabinets composed of IIoT components and cyber-physical systems, including: two SCADA systems (one proprietary and one from Siemens), fourteen advanced controllers from different vendors (Siemens, Schneider, Omron, among others), proprietary controllers deployed on IoT development boards (e.g. Intel Galileo, Arduinos, Raspberries), fifteen gateways with support for IoT and various industrial protocols (e.g. PROFINET, EtherNet/IP, EtherCAT, ModbusTCP, among others), nine industrial PCs, eight HMIs and three TVs as HMI interfaces, several readers (one optimal and RFID), dedicated servers for solution hybridization and deployment of a digital twin, IIoT development kits (WirelessHART and ISA100.11a), generic IoT sensors, several training mockups to illustrate industry-specific scenarios (e.g. robot and conveyor belt) and connection to a blockchain network.
Además, el laboratorio cuenta con una plataforma para el estudio de la seguridad aplicada a los entornos de gestión de estaciones de carga de vehículos eléctricos (EV, del inglés electrical vehicle), ofreciendo un «EV-Urban Lab» a la comunidad universitaria para la realización de experimentos. Esta plataforma incorpora una instancia de Firmware y una red de blockchain para volcar datos de las estaciones de recarga como el estado y los datos del usuario, y favorecer el análisis y los experimentos. Todas las redes desplegadas en blockchain en la infraestructura de ciberseguridad están diseñadas para ser permisionadas, basadas en tecnologías como Hyperledger Fabric, Hyperledger Besu, y Consensys Quorum. Asimismo, la infraestructura de ciberseguridad dispone de equipos especializados para el análisis forense de diversos dispositivos con herramientas software como IDA Pro, Encase Forensic Deluxe y AccessData Forensic Toolkit para ingeniería inversa, análisis de malware, recuperación de pruebas digitales y forense.
Big Data Infrastructure
The Big Data infrastructure provides a HW/SW environment for the development and deployment of Big Data analytics applications with a special application interest in the fields of health and agriculture. It was obtained through funding of 670,098€ from a singular infrastructure acquisition project [UNMA15-CE-3196] co-financed with FEDER funds (BOE 5 December 2017). Among its main HW features, it consists of a total of 688 cores (of which 384 cores are dedicated to computing tasks) provided by Intel Xeon Skylake Gold 6140 v5 processors (16 cores per processor, 2.10Ghz), 7.13 TB of RAM and 1.328 TB of storage
Currently, this infrastructure is being upgraded with the addition of new equipment that will add 384 cores (6 servers with 2 Intel Xeon Platinum 8358 processors with 32 cores at 2.6GHz each), 7 TB of RAM and 383 TB of storage to the existing one. The funding is 538,450€ through contract LifeWatch-2019-11- UMA-01, co-financed with FEDER funds for the operation “Environmental and Biodiversity Climate Change Lab (EnBiC2-Lab)” within the call for FEDER cofinanced operations (Pluriregional Operational Program of Spain 2014-2020)
This infrastructure provides a development environment for Big Data analytics applications based on the use of OpenStack and Docker containers to put services into production. It is currently being used for experimental studies using technologies such as Apache Spark, Kafka, Neo4J, MongoDB and Apache Hadoop. It includes tools and services (TITAN, BIGOWL) for the generation and deployment of Big Data workflows in both industry and research, and is the basis of Virtual Research Environments (VREs) for the orchestration of services in the development of e-Labs and e-Services. Other important services include multi-source semantic Web harmonization, biomedical data integration and analysis, Earth observation from satellite data (through the Copernicus program), and agro-environmental services processing and analysis.

FOG Computing Infraestructure
The Fog computing infrastructure provides a HW/SW environment for the development of critical applications with low latency requirements, with special emphasis on the application of artificial intelligence techniques, such as structural health monitoring. The infrastructure was obtained with FEDER co-financing [EQC2018-005016-P] in the call ayudas para la adquisición de equipamiento científico-técnico correspondientes al subprograma estatal de infraestructuras de investigación y equipamiento científico-técnico (plan estatal I+D+I 2017-2020) of 2018, with a total amount of 362,774.94€. Among the HW features, its 364 cores provided by Intel Xeon SP G6230R processors (26 cores, 2.1GHz), 448GB of graphics memory provided by NVIDIA V100 cards (5120 Cuda cores, 32GB RAM), 384GB of RAM and a total of 12.8TB of storage stand out. It also highlights its two portable Edge nodes with an Intel Xeon D2187NT processor (16 cores, 2GHz), an Nvidia T4 graphics card and its support for Wifi and LTE/4G wireless communications. Finally, the infrastructure has an embedded cluster composed of 48 Raspberry Pi 3 for the deployment of multiple orchestrated services on the edge.
The infrastructure provides a production environment through Kubernetes for the development of critical applications with low latency on top of Docker containers. These applications can make use of GPU acceleration for processing-intensive techniques such as machine learning. The infrastructure is currently being used in the context of several national and international research projects, including monitoring the structural health of civil infrastructures, digital twins of agricultural infrastructures and analyzing smart grids. Technologies in operation include tools such as Apache Kafka, InfluxDB, Eclipse Hono and RabbitMQ, and developed frameworks such as Kafka-ML, which allows the orchestration of data streams and machine learning frameworks.
Ex-scalable Laboratory Infraestructure
The Exascale Laboratory for Artificial Intelligence and Numerical Modeling is a high-performance parallel computing infrastructure composed of four NVIDIA DGX A100 interconnected by an InfiniBand network. It improves upon traditional approaches by unifying all Artificial Intelligence (AI) workloads, from analytics to training to inference. Each DGX A100 has eight GPUs with a total of 320 GB of memory (40 GB each GPU) with a GPU-toGPU direct bandwidth of 600 GB/s. It is specially designed for AI tasks that require extracting knowledge from large datasets (TB) with an unprecedent power that delivers the fastest time to solution, allowing to tackle challenges in an affordable timeframe.